The Australian Education System
The Australian Academic Year
The Australian academic year begins in late January or early February for school students, and runs to mid-December.
Students in Australia attend school for approximately 180 days per year; made up of four terms, each lasting around 10 weeks. The school year runs from late January until mid-December.
The summer holiday is from mid-December until late January and is the longest of the school breaks. The remaining terms are separated by two or three weeks of holiday.
The typical school day in Australia is from 9.00am until 3.30pm and lunch is eaten at school, with a shorter break in the mid morning. Many schools operate before and after school clubs to cater for working parents and also offer after school sporting and other activities.

Educational pathways in Australia
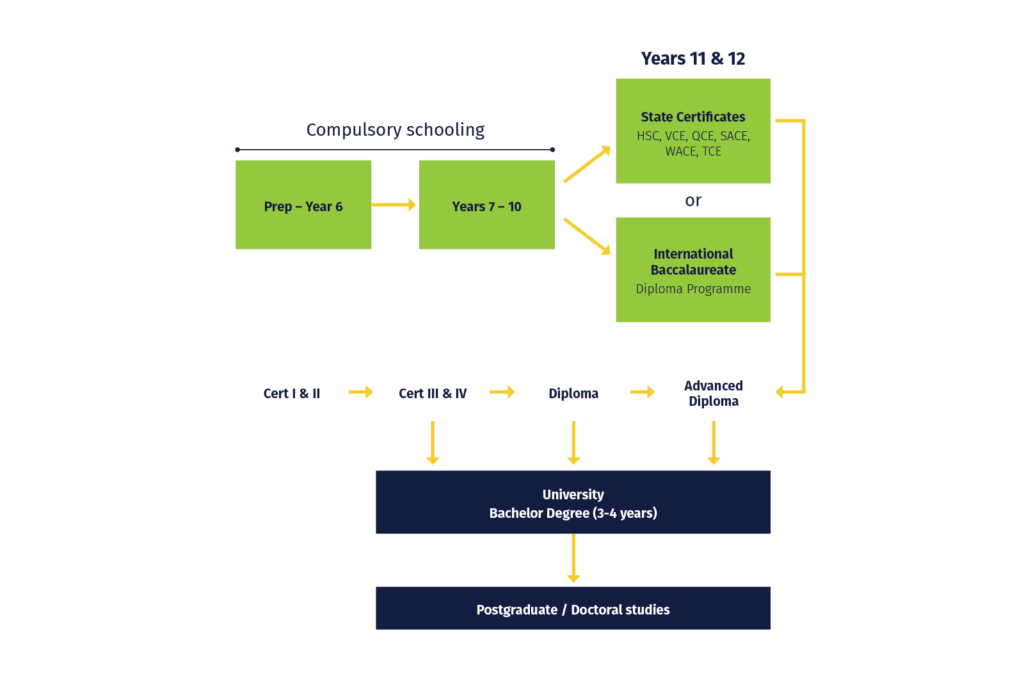
School education is similar across Australia. School education (primary and secondary) is compulsory between the ages of six and sixteen (Year 1 to Year 10).
School education is generally spread across 13 years and divided into:
- Primary school – seven years, starting at Kindergarten /Preparatory through to Year 6.
- Middle school – three years, from Years 7 to 9.
- Senior school – three years, Years 10 to 12.
Students who complete their senior secondary school program after Years 11 and 12 are awarded a Senior Secondary Certificate of Education. This certificate has different names in different states:
- VCE – Victorian Certificate of Education
- HSC – High School Certificate (New South Wales and ACT)
- QCE – Queensland Certificate of Education
- SACE – South Australian Certificate of Education
- TCE – Tasmanian Certificate of Education
- WACE – Western Australian Certificate of Education
Even though the certificates have different names, all students studying in Australian schools learn the Australian curriculum. The Australian Curriculum provides schools, teachers, parents and students a clear understanding of what students should learn. This curriculum applies no matter where a student lives or what school system they’re in.
In addition, there are a number of government and private schools in Australia offering the International Baccalaureate (IB), a two-year pre-university curriculum for students aged 16 to 19. These students receive an International Baccalaureate Diploma upon graduation.
The Australian Tertiary Admissions Rank
All students attending schools in Australia receive an Australian Tertiary Admissions Rank (ATAR) score upon completion of their high school certificate or IB Diploma.
The ATAR score is based on examination results and school assessed coursework with the top ATAR being 99.95. The ATAR is a percentile rank, not a score, and compares students within a given year.
The ATAR score is designed specifically to assist tertiary institutions in selecting applicants for some courses but not all courses require an ATAR score.
Universities use the ATAR to help them select students for their courses and admission to most tertiary courses is based on the selection rank. Some universities also use other criteria when selecting students (e.g. a personal statement, a questionnaire, a portfolio of work, an audition, an interview or a test).
Qualifications from Australian high schools are recognised worldwide. The ATAR is accepted internationally in many universities. Even top-ranked universities like Oxford and Cambridge recognise the ATAR score for admissions.
